Checkered gartersnakeThamnophis marcianus |

Custom Search
|
|
The Checkered garter snake or Checkered gartersnake (Thamnophis marcianus) is a colubrid mildly venomous snake species found in the southwestern United States southwards into Mexico and Central America as far south as Costa Rica. It is one of many species of garter snake.
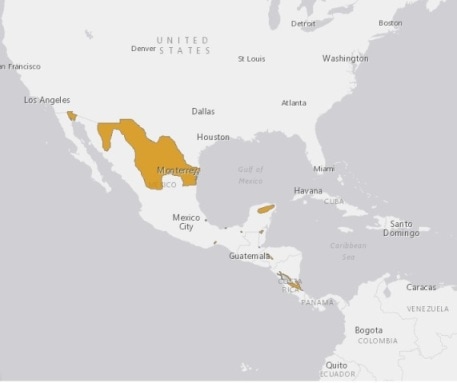
Their range extends from the southwestern United States including southern Arizona and southeastern California, Oklahoma, New Mexico, and southern Kansas and Texas. They are also found in northern and central Mexico with several disjunct populations found through central and southern Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Honduras, and Costa Rica. They are found at elevations from near sea level up to 7200 ft (2200 m) high. The checkered garter snake is found in a variety of habitats throughout its massive range from arid and semiarid regions and even deserts in California to grassland, pine-palmetto savanna, thornbush savanna, forests and tropical moist forests in Costa Rica. These snakes are usually found not very far from water including rivers, streams, ponds, springs, swamps, marshes, flooded areas, and irrigation ditches and canals. Sometimes the water source isn't visible above ground. They are usually active during the day in the northern regions of their range but may become nocturnal in the south to escape the hot temperatures during the day. The checkered garter snakes are good swimmers and may even dive to escape when disturbed. When handled they will excrete a foul smelling musk upon its aggressors, they will also bite but leave only tiny superficial bite marks.
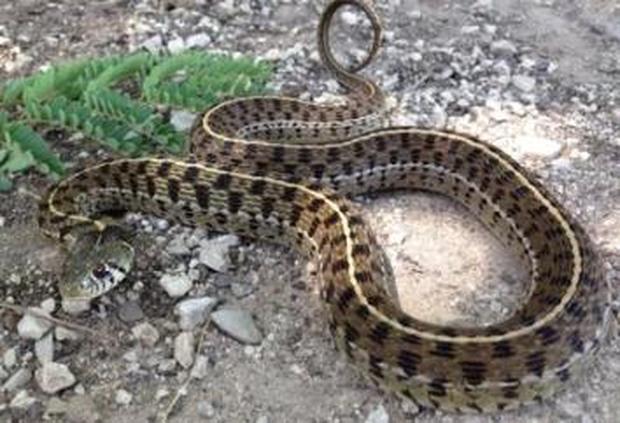
The checkered garter snake has large black blotches forming their distinctive checkerboard pattern over its usually tan, brown, olive or greenish body. Between the rows of checkers on the back and sides, there are usually 3 white or yellowish stripes, one on the middle and 2 on the sides.
There is a large black blotch on each side of the head placed behind 2 yellow or whitish crescents reaching the corner of the mouth. Their belly is normally pale in color usually without any markings but sometimes is blotched with black spots. These are medium-sized snakes reaching up 43 inches (slightly over 1 m) in maximum length, although on average they reach about 28 inches (71 cm). Their head isn't much wider and distinct from the neck. They have keeled dorsal scales and an undivided anal plate. The checkered garter snake is a popular pet snake and often sold in the reptile pet trade, they are considered quite hardy in captivity. The species is also bred in captivity with some albino form being produced. Subspecies / Taxonomy / Etymology
The species was first described by Baird and Girard in 1853. The species-specific epithet, "marcianus" given in honor of the American Brigadier General Randolph B. Marcy, who in the mid 19th century led surveying expeditions to the frontier. There are 3 subspecies currently recognized for the checkered garter snake. Northern Checkered Garter Snake (Thamnophis marcianus marcianus - Baird & Girard, 1853) - Found in the USA and northern Mexico. This subspecies is also known as Marcy’s Checkered Garter Snake and is often found in the exotic pet trade, with an albino morph being very popular. Nicaraguan Checkered Garter Snake (Thamnophis marcianus bovallii - Dunn, 1940) - Found only in Nicaragua. Yucatan Checkered Garter Snake (Thamnophis marcianus praeocularis - Bocourt, 1892) - This subspecies if found on the in Belize, Honduras, Guatemala and Yucatan Peninsula. Venom / Bite Like other garter snake species they have toxins in their saliva with effects similar to snake venom. Their bite can produce a mild reaction in humans, but they are considered harmless and not dangerous to humans. Similar to other garter snake species like California Red-Sided gartersnake it needs to “chew” on the prey, so the venom is delivered into the blood. Contrary to other venomous snakes like the pit vipers capable of injecting venom very deep into the prey using their long and hollow fangs. Diet / Feeding Checkered garter snakes feed on a variety of animals including small mammals, frogs, toads, tadpoles, salamanders, lizards, other snakes, earthworms, crayfish, fish, and even insects. Sometimes they will even eat carrion from the roadway kill. They will actively forage to find prey. Reproduction The checkered gartersnake is a live-bearing snake or viviparous. The gestation period normally lasts between 80 and 105 days. Females give birth to live young in the spring or summer from May to October. Usually, a clutch averages around 6 to 8 younglings but it may be as high as 35. The newborn snakes are 8 or 9 inches long at birth. Conservation / Threats Listed as "Least Concern" because these snakes are widely distributed and relatively common at least in the northern part of its range. In North America, there are no major threats to the Checkered Garter Snake, but they are listed as threatened in Kansas. However, subpopulations sound in southern Mexico and Central America are threatened by habitat conversion for agriculture with the use of pesticides leading to declining amphibian populations which these snakes feed on. Because of this, the species has become less common, and its distribution fragmented and disjunct in southern Mexico and Central America.
|
Scientific classification |
© 2014 Snake Facts About Us | Privacy Policy | Contact