What do Snakes Eat? |

Custom Search
|
Snakes are very diverse when it comes to size, ranging from small species just a few inches long the like the thread snake to the biggest snakes in the world like pythons and anacondas.
These very different types of snakes will obviously eat different things. Smaller snake species will feed on smaller animals, including insects, rodents, birds and their eggs, fish, frogs, lizards and small mammals. The bigger the snake the larger the animals they eat, big constrictors like the green anaconda or the reticulated python have been known to eat deer and pigs! These giant snakes can even take down crocodiles and alligators. Although some snakes have evolved to feed on a generalist diet like the eastern indigo snake, some species have special diets like the egg-eating snake that only eats eggs. While other snakes are known for eating other snakes, like the king cobra or king snakes like the California kingsnake. Snakes form a diverse group and have developed many different hunting strategies, adapted to their own size and habitat they live in. Some snake species will actively hunt their prey like the blue racer. Other snakes will lie hidden waiting to ambush prey, relying on their camouflage like the puff adder. While the desert dwelling sidewinder hides under the sand waiting for some animal to pass by. They will go as far as using tricks to fool unsuspecting victims to come closer to them. For instance, juvenile cottonmouth snakes have a bright yellow tip on its tail to look like a worm they use to lure prey.
How do snakes kill and eat their prey?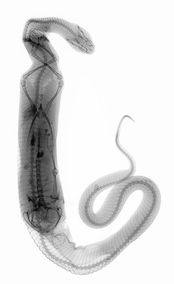
Snakes kill their prey mainly in 2 ways, depending if they are venomous snakes or non-venomous snakes.
Venomous snakes like the inland taipan will strike and sink their fangs into the prey injecting venom to paralyze or kill it before swallowing it. Some snake venom contain hemotoxins that break down cells and tissues in the victim and help digesting prey. While most non-venomous snakes are constrictors that wrap their bodies around the prey and slowly tighten their coils to squeeze the life out of their prey by stopping their heart. Some will just grab an animal overpowering it and eating it alive and others will squash the prey into the walls of their burrows. Even though snakes do have teeth, they are made for grabbing and holding prey, not for chewing food, for that reason snakes have to swallow their food whole. But how do snakes swallow such impossibly big meals without chewing, well they have very flexible jaws capable of unhinging, so they can have their mouths open wide. They also have very powerful muscles along their bodies and use them for moving as well as swallowing food. These muscles move the food down into the snake’s stomach, a process that can last a few minutes to more than an hour, depending on the size of the meal the snake is eating. Once in the snake’s stomach a meal can take anywhere from a few days, several weeks to a couple of months to be fully digested, that's one of the reasons why some snake species need to feed only a few times every year! When the digestion is complete, the snake will vomit any undigested parts like bones or hooves. How much do snakes eat?
For any given weight snakes eat much less than a mammal of similar size, this is because snakes are cold-blooded reptiles.
While mammals need to eat so they can generate energy to maintain their body temperature, snakes don't and use only about 10% of the energy when compared to mammals. So snakes need to eat much less than mammals, about 10 times less. Just like food snakes also drink much less water than a mammal of the same size.
|
Did You Know?
The Rinkhals or ring-necked spitting cobra is capable of spitting venom to a distance of 2 or 3 meters. |
© 2014 Snake Facts About Us | Privacy Policy | Contact






