Mangrove SnakeBoiga dendrophila |

Custom Search
|
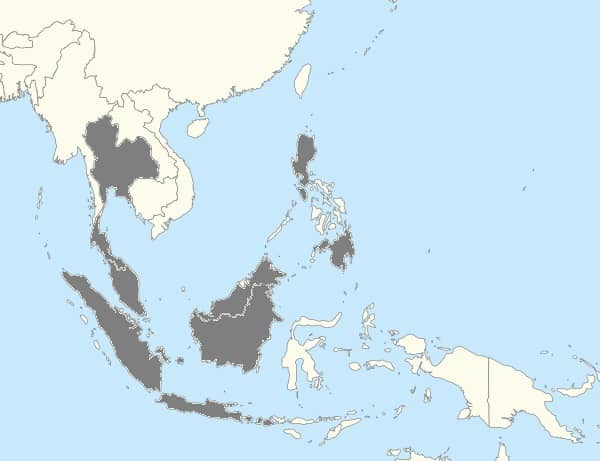
The mangrove snakes are found in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, Vietnam, Cambodia and Philippines.
They belong to the Boiga genus, the cat-eyed snakes or cat snakes, this genus of the family Colubridae is comprised of more than 30 species. They are one of the largest cat snake species, averaging between 6 and 8 feet (1.8 to 2.4 m) in length. The mangrove snake upper body is jet black and covered with thin yellow and evenly spaced stripes, sometimes these bands meet at the top of the body. The chin and throat area are bright yellow, and the inside of the mouth is whitish, much like the cottonmouth (Agkistrodon piscivorus). They have large eyes with vertical pupils similar to those of cats, it's obvious where some of their common names derive from. Despite their common name the mangrove snake inhabits coastal both lowland forests and mangrove swamps found throughout their tropical and subtropical range. These snakes can be found both near fresh or brackish water bodies. These snakes are mostly active at night by day they lie motionless on overhanging tree branches.The mangrove snake is also a very capable swimmer. The mangrove snakes are sometimes misidentified and confused with the deadly Banded Krait (Bungarus fasciatus) where their range overlaps.
Species / Taxonomy
Within this species like in many other snakes, there's some debate about the actual number of subspecies, ranging between 8 and 10 recognized subspecies. Some researchers have even recommended that certain subspecies be elevated to full species status, while other scientists think that even more subspecies must be recognized. These are the 9 subspecies commonly recognized as being valid by scientists. Boiga dendrophila dendrophila (F. Boie, 1827) – Found in Indonesia Java island. Boiga dendrophila annectens (Boulenger, 1896) – Found in Indonesia Kalimantan region, Brunei and East Malaysia. Boiga dendrophila divergens (Taylor, 1922) – Found in the Philippines Luzon and Polillo islands. Boiga dendrophila gemmicincta (A.M.C. Duméril, Bibron & A.H.A. Duméril, 1854) – Found in Indonesian Sulawesi island. Boiga dendrophila latifasciata (Boulenger, 1896) – Found in the Philippines Mindanao island. Boiga dendrophila levitoni (Gaulke, Demegillo, G. Vogel, 2005) – Found in Panay island, and probably in other islands of the West Visayas region. Boiga dendrophila melanota (Boulenger, 1896) – Found in southern Thailand, West Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesian Sumatra island. Boiga dendrophila multicincta (Boulenger, 1896) – Found in Philippines Balabac island. Boiga dendrophila occidentalis (Brongersma, 1934) – Found in Indonesia. Venom / Bite
The mangrove snake is a rear-fanged species and considered only mildly venomous, and there has never been a confirmed human fatality. Unlike pit vipers or cobras rear-fanged snake's venom delivery system doesn't possess a highly developed venom gland, duct system or hollow fangs. The mangrove snake only has slightly enlarged rear teeth that must puncture the skin to allow venom to enter the open wound. These "fangs" have grooves and are angled backward, making somewhat easier for the venom to enter the bite wound. But their fangs are also small making it difficult to deliver a bite on a human arm or leg, and inject the venom efficiently. Sometimes to efficiently transfer the venom into even a small animal they actually have to chew on their prey. Even so moderate envenomations in humans resulting in intense swelling, skin discoloration, strong bleeding and painful wounds have been reported. Even though these appear to be quite docile beatiful snakes some specimens have an unpredictable temperament and will readily bite. Like other venomous snakes there's ongoing research of its venom. In the future it maybe used to develop treatments to cardiovascular disease or cancer, and one day may save human lives. Diet / Feeding The mangrove snakes becomes active at night descending to the ground from their basking overhanging branches to hunt. They are opportunistic predators that feed on rodents, small birds and their eggs, fish, bats, frogs and sometimes even feed on other snakes. Juvenile snakes prey mostly on small lizards or frogs and on occasion large slugs.. They use their venom to immobilize the prey, it's mild venom may be harmless to humans, but it is very effective against the smaller animals on which they feed. Reproduction These snakes are oviparous, which means the mangrove snake is an egg layer species, females lay clutches averaging 4 to 15 eggs that hatch after an incubation period of about 12 weeks. The hatchlings measure about 35 to 43 cm and resemble adult snakes in both coloration and pattern. Conservation / Threats The mangrove snake is not yet evaluated by the IUCN.
|
Scientific classification |
© 2014 Snake Facts About Us | Privacy Policy | Contact