European Cat SnakeTelescopus fallax |

Custom Search
|
|
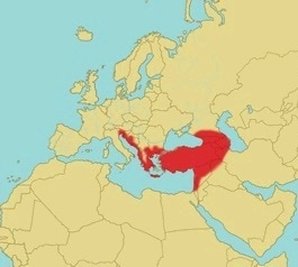
The European cat snake or European Catsnake (Telescopus fallax) sometimes called simply cat snake is a mildly venomous colubrid snake species found in many countries in the Caucasus and Mediterranean regions.
Their range extends from extreme northeastern Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, southern Montenegro, southern Bulgaria, Albania, Macedonia, Greece, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, Iran, Iraq, and Israel in the south. The species is found in the Caucasus Mountains including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia and southern Russia (Republic of Dagestan). It's also found on the islands of Malta and Cyprus. These cat snakes can be found in a variety of habitats including rocky terrain, woodlands, and even beaches usually with some scrub or bush vegetation. Sometimes they are found in residential areas close to human habitations. Other populations in its extensive range inhabit steppes, semi-deserts and sometimes on the edges of mountain forests. They are found at elevations up to about 6500 ft (2000 m). The European cat snake is a great climber and often found climbing trees or walls. These are small to medium snakes, with a slender and more or less cylindrical body and a rather short tail. The European cat snake grows to a maximum length of about 4 feet (120 cm) but on average they reach only about 24 inches (60 cm). Their coloration varies with geographic range and among specimens, matching their surroundings to provide camouflage. They usually have a gold, tan, gray or light brown background color covered with darker blotches or crossbands on the back. The head is flat, short, oval in shape and distinct from the neck. Their dorsal scales are smooth and the ventral scales are rounded. They have fairly small to medium eyes with vertical and elliptical pupils similar to those of cats, hence the species common name.
The European cat snake is a crepuscular and nocturnal species and while by day their pupils contract to narrow vertical slits at night the pupils will expand to let more light in. They belong to the Cat snakes group, comprised of several arboreal or semi-arboreal rear-fanged snakes in the family Colubridae.
The species and its subspecies are also known by other common names such as the Soosan snake, European Tiger Snake, Mediterranean Cat Snake, Caucasian Cat Snake, Many-scaled Cat Snake, Cretan Cat snake, Cat-eyed snake or simply Cat Snake. Subspecies / Taxonomy The European cat snake was first described by Fleischmann in 1831. There are 7 subspecies currently recognized. Telescopus fallax fallax (Fleischmann - 1831) - Found in northeastern Italy, in several Greek islands including Paros, Mykonos, Antiparos, Crete, Kalymnos, Samos, Kimolos, Milos, Corfu, Syros), Albania, coastal Croatia (including some Adriatic islands), Slovenia, Herzegovina, Monte Negro, Macedonia, southern Bulgaria, Turkey, Malta, Cyprus, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Israel, Southern Russia , Armenia, Republic of Georgia and Azerbaijan. Telescopus fallax iberus (Eichwald - 1831) - Found on Armenia, Azerbaijan, South Georgia, southern Russia, northern Iran, and East Turkey. Telescopus fallax intermedius (Gruber - 1974) - Found on Antikythira, a Greek island on the edge of the Aegean Sea. Telescopus fallax multisquamatus (Wettstein - 1952) - Found on Koufonisia a Greek island. Telescopus fallax pallidus (Stepanek - 1944) - This subspecies inhabits Crete, Gavdos, Elasa and Christiana islands. Telescopus fallax syriacus (Boettger - 1889) - Found in Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, southeast Turkey and northern Israel. Telescopus fallax cyprianus (Barbour & Amaral - 1927) - This subspecies is found only in Cyprus. Venom / Bite
The European cat snake is considered only a mildly venomous snake species and not dangerous to humans. This is a rear-fanged type of snake, with the grooved fangs located at the back of the upper jaw. They rarely bite and seldom inject venom in defensive bites. Most likely its bite would cause probably only some minor local pain and swelling, and if not properly disinfected eventually an infection. Diet / Feeding The European cat snake main source of food are small geckos and lizards, but they eat also small mammals and even birds. Younger snakes will also eat invertebrates. Their mild venom is used more as a means of relaxing the prey body helping the snake to subdue it and not actually to kill the prey. Reproduction These are oviparous snakes meaning that European cat snake females lay eggs in clutches ranging from 5 to 9 eggs. The eggs usually hatch in late summer or early autumn. Conservation / Threats The European cat snake is listed as a "Least Concern" species due to its wide distribution and presumed large population in the wild. They also inhabit a number of protected areas. Even so, they are sometimes killed in some parts of its range where they are confused with more dangerous venomous vipers. While in other regions they are threatened by habitat destruction and degradation due to urbanization and conversion of land to agricultural use. These snakes are also victims of road mortality.
|
Did You Know?
The central ranges taipan a large, fast and highly venomous species of taipan was only discovered and described in 2007. Scientific classification |
© 2014 Snake Facts About Us | Privacy Policy | Contact